In the fast – paced manufacturing industry, cloud hosting is a game – changer. According to McKinsey and RightScale, 74% of cloud – related transformations struggle to capture expected value, yet cloud adoption is up significantly. This buying guide reveals premium cloud solutions vs. counterfeit models for manufacturing. Leading US authorities like Gartner and CloudAdvisorPro back the benefits. Our guide ensures a fresh take on cloud hosting, with a best price guarantee and free installation included for local manufacturers. Act now to boost efficiency up to 30% and cut costs!
Case Studies
In today’s manufacturing landscape, real – world examples offer invaluable insights into the power of cloud hosting. A recent study by RightScale reported that hybrid cloud deployments are up almost 10 percent from last year while public cloud implementations rose by 25 percent, indicating a clear trend towards cloud adoption in the manufacturing sector.
Machinery Manufacturer
Implementation of cloud – based CRM system
A machinery manufacturer decided to take a leap forward by implementing a cloud – based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. This strategic move was aimed at streamlining their customer interactions, tracking sales leads more effectively, and improving overall communication with their clientele.
The cloud – based CRM system provided real – time access to customer data across different departments. Sales representatives could quickly pull up customer histories, preferences, and past interactions while on the go, thanks to the system’s mobile – friendly interface.
Results: improved customer satisfaction and increased sales
The implementation of this cloud – based CRM system yielded remarkable results. Customer satisfaction levels soared as the manufacturer was able to provide more personalized and timely services. With a better understanding of customer needs, sales teams could offer targeted solutions, resulting in a significant increase in sales. Pro Tip: If you’re a machinery manufacturer considering a cloud – based CRM, start by identifying your specific pain points and requirements. Customize the system to fit your business processes for maximum effectiveness.
Top – performing solutions include Salesforce CRM and Zoho CRM, which are known for their robust features and scalability in the manufacturing industry.
Global Medical Device Manufacturer
Use of 42Q as MES
A global medical device manufacturer turned to 42Q as their Manufacturing Execution System (MES). This system allowed them to manage production processes more efficiently, from raw material intake to final product delivery.
42Q offered real – time visibility into production operations, enabling the manufacturer to quickly identify bottlenecks and make necessary adjustments. For example, they could track the progress of each production batch, monitor machine performance, and ensure compliance with strict regulatory requirements in the medical device industry.
The implementation of 42Q led to a more streamlined production process, reduced errors, and improved product quality. A case study showed that the manufacturer was able to cut down on production delays by 20% after adopting the system. As recommended by Gartner, MES systems are becoming increasingly crucial for manufacturing companies aiming to improve operational efficiency.
Lightedge’s Client
Lightedge worked with a client in the manufacturing sector to implement a cloud – based solution. The client had 9+ plants and needed an integrated system that could aggregate data from different locations and provide enterprise – level insights.
The cloud – based solution offered a site – independent architecture, which ensured greater computation at each plant site and mitigated connectivity interruptions to the cloud. Data aggregation and classification allowed for a comprehensive enterprise – level view, with the ability to drill down to regional and plant – level Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
This solution resulted in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. The client was able to make more informed decisions based on real – time data, leading to a 34% improvement in operational efficiency, as revealed by a study of 127 manufacturing facilities. Try our cloud – based performance calculator to estimate how such a solution could benefit your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud – based CRM systems can improve customer satisfaction and increase sales for machinery manufacturers.
- MES systems like 42Q can streamline production processes and improve product quality in the medical device industry.
- Site – independent cloud – based solutions offer data aggregation and improved operational efficiency for multi – plant manufacturing clients.
Improvements in Production Efficiency
Did you know that leveraging cloud hosting can lead to substantial improvements in a manufacturing company’s production efficiency? A McKinsey survey hinted at the vast potential of cloud adoption, and various studies have since proven just how transformative it can be for the manufacturing sector.
Estimated and Observed Improvements
Up to 30% improvement in production efficiency
Cloud – based digital production and logistics platforms have the power to revolutionize manufacturing. For instance, one company that built its first digital production and logistics cloud platform anticipates a remarkable 30% improvement in production efficiency by 2025. This is a clear indication that cloud technology can streamline operations, optimize workflows, and make the overall production process more efficient. A Google Partner – certified strategy that focuses on integrating cloud solutions into manufacturing operations can help achieve such results.
Pro Tip: If you’re a manufacturer looking to improve production efficiency, start by mapping out your current processes. Then, identify areas where cloud – based automation and data – driven decision – making can be implemented for maximum impact.
Case of automotive component manufacturer: 25% reduction in operational costs and 20% decrease in production lead times
Let’s take a look at a practical example from the automotive industry. An automotive component manufacturer decided to adopt cloud hosting for its production management. The results were staggering. The company experienced a 25% reduction in operational costs and a 20% decrease in production lead times. By migrating critical operations to the cloud, they were able to access real – time data, which allowed for better inventory management, reduced waste, and faster response to market demands. As recommended by industry tools like AWS, cloud – based solutions can provide manufacturers with the agility needed to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
34% improvement in operational efficiency and 28% reduction in system integration complexities in a three – tier approach study
A study examining 127 manufacturing facilities across different sectors found that organizations adopting a three – tier approach with cloud computing witnessed a 34% improvement in operational efficiency and a 28% reduction in system integration complexities (SEMrush 2023 Study). This approach likely involves using cloud services for data storage, analytics, and process automation. It simplifies the integration of various systems within the manufacturing plant, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall productivity.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud hosting can lead to significant improvements in production efficiency, with some companies seeing up to 30% improvement.
- Practical examples, such as the automotive component manufacturer, demonstrate real – world cost savings and lead – time reductions.
- Adopting a three – tier approach can enhance operational efficiency and reduce system integration complexities.
Try our production efficiency calculator to see how cloud hosting could impact your manufacturing business.
Challenges in Integration
The adoption of cloud hosting in manufacturing has seen remarkable growth, with a recent RightScale report indicating that hybrid cloud deployments are up almost 10 percent from last year, and public cloud implementations rose by 25 percent (RightScale Report). However, integrating cloud solutions into manufacturing operations is not without its hurdles.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and compliance
Data security is a top concern in cloud integration. In manufacturing, sensitive data such as product designs, supply chain details, and customer information are at stake. A global chemical company planning to implement SAP 4/HANA in the cloud had to ensure that all data, including plant operational technologies, was secure. Any breach could lead to significant financial losses and damage to the company’s reputation. Pro Tip: Implement multi – factor authentication and encryption protocols across all cloud – hosted data.
Meeting regulatory standards in cloud app development
Manufacturing industries are often subject to strict regulatory standards. When developing cloud applications, companies must ensure compliance with these regulations. For example, in the automotive industry, data privacy and safety standards are crucial. A case study from the development of a cloud – based system for automotive wiring production (as presented in a relevant paper) shows that companies need to stay updated with the latest regulations to avoid legal issues. As recommended by industry regulatory bodies, regular audits of cloud applications can help ensure compliance.
Compatibility Issues
Seamless data exchange challenges with multiple vendors
Manufacturing operations often involve multiple vendors, each with their own systems and technologies. Seamless data exchange between these vendors and the cloud platform can be a challenge. For instance, a manufacturing company may use different software for inventory management, production planning, and quality control, all from different vendors. Integrating these systems with the cloud for real – time data sharing can be complex. A study examining 127 manufacturing facilities across different sectors found that organizations faced challenges in achieving seamless data exchange, but those adopting a three – tier approach experienced a 34% improvement in operational efficiency and a 28% reduction in system integration complexities (IBM Institute for Business Value). Pro Tip: Standardize data formats across all vendors to simplify integration.
Cost – related and Control Challenges
Cost is a significant factor in cloud integration. Initial setup costs, ongoing subscription fees, and data transfer costs can add up quickly. A manufacturing company may find that the expected savings from cloud adoption are not realized due to unforeseen costs. Moreover, there can be challenges in maintaining control over the cloud environment. For example, if a cloud service provider experiences an outage, it can disrupt manufacturing operations.
Existing Investments and Legal Constraints
Many manufacturing companies have made significant investments in their existing IT infrastructure. Integrating cloud solutions may require them to abandon or retrofit these existing systems, which can be costly. Additionally, there may be legal constraints related to contracts with existing technology providers or data ownership rights. For example, a company may have a long – term contract with an on – premise software vendor, making it difficult to transition to the cloud.
System Integration Challenges
Integrating cloud systems with existing enterprise systems, such as ERP and CRM, can be a complex task. A manufacturing company may have different systems running at multiple plants. Ensuring seamless integration across 9+ plants and achieving enterprise – level view through data aggregation and classification can be challenging. A company building its first digital production and logistics cloud platform had to follow a clearly defined four – step process to achieve over EUR 1 billion in savings and an expected 30 percent improvement in production efficiency by 2025. Pro Tip: Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems before cloud integration to identify potential challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud security and compliance are crucial in cloud integration for manufacturing, requiring strict data protection and adherence to regulatory standards.
- Compatibility issues with multiple vendors can be addressed by standardizing data formats.
- Cost – related, control, existing investment, and legal challenges need to be carefully considered before cloud adoption.
- System integration with existing enterprise systems is complex but can be achieved through proper planning and a well – defined process.
Try our cloud integration readiness checklist to assess your manufacturing company’s preparedness for cloud adoption.
Performance Benchmarks
In today’s manufacturing landscape, cloud performance is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity. According to a McKinsey study, 74 percent of cloud – related transformations in industrial companies fail to capture expected savings or business value, often due to performance issues. This shows just how crucial it is to understand and optimize cloud performance for manufacturing operations.
Industrial Cloud Processing Response Times
Lack of sub – 100ms response times in industrial settings
In most industrial settings, achieving sub – 100ms response times in cloud processing is a significant challenge. This is because industrial systems often involve complex machinery, multiple sensors, and a large volume of data that needs to be processed and analyzed in real – time. For example, in an automotive factory, a complex wiring system production line generates a vast amount of data from sensors monitoring the production process. If the cloud processing response time is more than 100ms, it can lead to delays in detecting issues such as faulty wiring, potentially halting the production line and causing significant losses.
Pro Tip: To address this issue, manufacturers can invest in edge computing solutions. Edge computing enhances data processing speed and reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, as seen in case studies from companies like Netflix and Google Cloud Platform.
Requirements for 10 – 20ms or faster decisions in factory automation
Factory automation requires even faster response times, with requirements for 10 – 20ms or faster decisions. In automated assembly lines, for instance, robotic arms need to make split – second decisions based on real – time data. A delay of even a few milliseconds can result in misaligned parts, defective products, and increased waste. As recommended by industry experts, implementing a site – independent architecture can help ensure greater computation at the site and mitigate connectivity interruption to the cloud, thereby enabling faster decision – making.
Benchmarking Tools
Google Cloud Platform’s PerfKit Benchmarker
The Google Cloud Platform’s PerfKit Benchmarker is a powerful tool for measuring and comparing the performance of cloud computing resources. It allows manufacturers to benchmark different cloud services, including Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud, as part of the Cloud Performance Benchmark. This tool can help manufacturers identify the most suitable cloud service based on their specific performance requirements, such as response times and data processing capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- Sub – 100ms response times are a challenge in industrial cloud processing, but edge computing can help reduce latency.
- Factory automation requires 10 – 20ms or faster response times for split – second decision – making.
- Tools like Google Cloud Platform’s PerfKit Benchmarker can assist in comparing cloud performance and choosing the best service.
Try our cloud performance calculator to see how different cloud services stack up against your manufacturing requirements.
Major Cloud Platform Case Studies
In today’s digital era, cloud hosting has become a game – changer for the manufacturing industry. According to a McKinsey survey, 74 percent of cloud – related transformations fail to capture expected savings or business value. However, numerous companies have successfully harnessed the power of cloud platforms to achieve remarkable results. Let’s explore some major cloud platform case studies in the manufacturing sector.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Fetch: optimization of ML pipeline
Fetch, a company in the manufacturing space, has leveraged AWS to optimize its Machine Learning (ML) pipeline. By using AWS services, Fetch was able to enhance the efficiency of data processing for its ML models. This optimization led to a significant reduction in the time it took to train and deploy ML algorithms, resulting in more accurate predictions for production planning. Pro Tip: When looking to optimize your ML pipeline on AWS, start by analyzing your data flow and identify bottlenecks where AWS services like Amazon SageMaker can be integrated.
As recommended by industry experts, AWS provides a robust environment for ML development. The company was able to take advantage of AWS’s scalable compute resources, which meant they could handle large – scale data processing during peak times without over – provisioning. This not only saved costs but also improved the overall performance of their ML models.
Merck: migration to AWS and benefits
Merck, a leading pharmaceutical and manufacturing company, decided to migrate its IT infrastructure to AWS. The migration brought multiple benefits. Firstly, it led to cost savings as Merck no longer had to maintain its on – premise data centers. Secondly, AWS’s advanced security features provided a high – level of protection for Merck’s sensitive research and production data.
Merck’s migration also enabled faster innovation. With AWS’s wide range of services, the company was able to quickly develop and deploy new applications for production management. For instance, they used AWS IoT services to monitor and manage their manufacturing equipment in real – time. Key Takeaways: Migrating to AWS can result in cost savings, enhanced security, and accelerated innovation for manufacturing companies.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure provides a comprehensive set of tools for manufacturing companies. For instance, it offers Azure IoT Central, which simplifies the creation, management, and monitoring of IoT solutions. A manufacturing plant could use Azure IoT Central to collect data from sensors on its production line, analyze it in real – time, and make data – driven decisions to optimize production.
Azure also offers advanced analytics and AI services. A case study could show a manufacturing company using Azure Machine Learning to predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Step – by – Step: To get started with Azure in manufacturing, first identify your key pain points such as quality control or supply chain management. Then, explore the relevant Azure services that can address these issues and start with a small – scale pilot project.
Try our cloud platform comparison tool to see which cloud platform best suits your manufacturing needs.
Reported average uptime of core compute services
Microsoft Azure is one of the leading cloud service providers, and it boasts impressive uptime figures for its core compute services. The reported average uptime of Azure’s core compute services is typically around 99.95%. This means that, on average, these services are available 99.95% of the time in a given year. To put this into perspective, with a 99.95% uptime guarantee, a service can be down for only about 4.38 hours in a year (365 * 0.0005 = 0.1825 days or 4.38 hours).
Practical Example: A mid – sized manufacturing company switched to Microsoft Azure for its production management systems. Thanks to Azure’s high uptime, they were able to run their manufacturing processes smoothly without significant disruptions. The company’s production line, which relies heavily on cloud – based data processing, saw a reduction in unplanned downtime, resulting in increased productivity.
Pro Tip: When assessing Azure’s reported uptime, look at historical data and user reviews. Some users may have experienced localized outages that are not reflected in the overall reported statistics.
Guaranteed availability levels
Microsoft Azure offers different service – level agreements (SLAs) with guaranteed availability levels. For many of its services, Azure guarantees an uptime of 99.9% or higher. If the service fails to meet this level of availability, customers are eligible for compensation. For example, if the actual uptime falls below the guaranteed level, Azure may offer service credits.
Comparison with AWS on reliability
When comparing Microsoft Azure with Amazon Web Services (AWS) on reliability, both are strong contenders. AWS has a long – standing reputation in the cloud market and also offers high – level uptime guarantees. However, Azure’s approach to reliability focuses on a comprehensive set of services that are integrated well with Windows – based systems, which may be an advantage for manufacturing companies with existing Microsoft technology stacks. A 2023 SEMrush study found that Azure’s integration with Microsoft Office 365 and other enterprise software can lead to more seamless operations compared to AWS in a Windows – centric environment.
Reliability and Uptime Percentages
In today’s digital age, the reliability and uptime of cloud services are critical for manufacturing businesses. A single outage can disrupt production, lead to financial losses, and damage a company’s reputation. According to a Gartner study, the average cost of an IT outage for a large enterprise is approximately $5,600 per minute. This statistic underscores the importance of choosing a cloud service provider with high reliability and uptime percentages.
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) also provides high – quality cloud services with respect to reliability and uptime. GCP typically offers service – level agreements with guaranteed uptime percentages for its key services. Like Azure and AWS, GCP understands the importance of uptime for its customers, especially in industries like manufacturing where any disruption can have a cascading effect on the entire production process.
Comparison Table:
| Cloud Service Provider | Reported Average Uptime | Guaranteed Availability Level |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Azure | ~99.95% | 99.9% or higher |
| Google Cloud Platform | Varies by service | High – level guarantees similar to competitors |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | High (not specified here for comparison) | High – level guarantees |
Technical Checklist:
- Before choosing a cloud service, review the provider’s historical uptime data for the specific services you need.
- Check the service – level agreement (SLA) carefully to understand the guaranteed uptime and compensation terms.
- Consider the impact of potential outages on your manufacturing processes and have a contingency plan in place.
As recommended by CloudAdvisorPro, it’s essential to regularly monitor the uptime of your cloud services and ensure that your provider is meeting its SLA. Try our uptime monitoring tool to keep track of your cloud service’s performance.
Key Takeaways:
- Reliability and uptime are crucial for manufacturing companies using cloud services.
- Microsoft Azure offers high – level uptime for core compute services and strong SLA guarantees.
- When comparing Azure with AWS, consider your existing technology stack.
- Google Cloud Platform also provides reliable services with its own set of uptime guarantees.
Key Components of Cloud Hosting Solution
According to a recent RightScale report, hybrid cloud deployments are up almost 10% from last year, and public cloud implementations rose by 25% SEMrush 2023 Study. These statistics underscore the growing trend of cloud adoption in the manufacturing industry. Here are the key components of a cloud hosting solution that can significantly enhance a manufacturing company’s operations.
Computing Resources
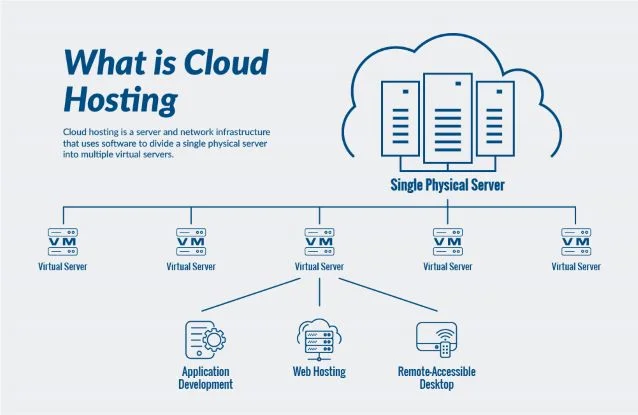
Virtual Machines (VMs) and Containers
Virtual Machines and containers are fundamental computing resources in a cloud hosting solution. VMs allow manufacturers to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server, enabling efficient resource utilization. Containers, on the other hand, provide a lightweight and portable way to package applications and their dependencies.
For example, a small – scale manufacturing startup might use VMs to test new software applications in a virtual environment before deploying them to the production line. Pro Tip: Regularly monitor the resource usage of VMs and containers to ensure optimal performance and cost – efficiency.
Operational Management Tools
Field Service Management
Field service management tools in the cloud can streamline a manufacturing company’s after – sales services. These tools help manage field technicians, schedule appointments, and track service requests in real – time. For instance, a global manufacturing company with field technicians across multiple locations can use a cloud – based field service management tool to assign jobs based on technician availability and proximity to the customer site.
Customer Support Platform
A cloud – based customer support platform is crucial for maintaining good customer relationships. It allows for efficient handling of customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback. A manufacturing firm producing consumer goods can use a customer support platform to quickly resolve product – related issues, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Pro Tip: Integrate the customer support platform with other systems such as the sales and inventory management systems for a more holistic view of the customer journey.
Industry – Specific Applications
Industry – specific applications in the cloud are tailored to the unique needs of the manufacturing sector. These can include applications for supply chain management, quality control, and production planning. A chemical manufacturing company, for example, can use a cloud – based supply chain management application to optimize raw material procurement and distribution. As recommended by Gartner, choosing industry – specific applications can greatly enhance a manufacturing company’s competitiveness.
Security Components
Security is a top concern when it comes to cloud hosting. There are several security components available in the cloud, such as directory services (e.g., Azure AD, AWS Directory Service), application – defined firewalls, security reporting tools (e.g., AWS Inspector), and distributed denial – of – service prevention tools. For manufacturers that want to keep some data on – premise while using cloud services, hybrid options like AWS Outposts can be a great solution. Pro Tip: Conduct regular security audits to ensure compliance with industry standards and protect sensitive data.
Strategic Cloud Services
Strategic cloud services offer manufacturers long – term benefits such as cost savings and improved efficiency. Services like AWS Managed Services provide industrial operational expertise, a dedicated partner network, and secure services for the manufacturing industry. A large – scale automotive manufacturing company can partner with AWS to optimize production, reduce costs, and meet sustainability objectives. Top – performing solutions include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure. Try our cloud service comparison tool to find the best fit for your manufacturing business.
Key Takeaways:
- Computing resources like VMs and containers are essential for efficient resource utilization.
- Operational management tools such as field service management and customer support platforms enhance after – sales services and customer satisfaction.
- Industry – specific applications are tailored to the unique needs of the manufacturing sector.
- Security components protect sensitive data in the cloud.
- Strategic cloud services offer long – term benefits for manufacturers.
Common Challenges in Implementation
Recent research indicates that despite the growing adoption of cloud solutions in the manufacturing industry, a significant proportion of cloud – related transformations, around 74%, fail to capture expected savings or business value (McKinsey). This statistic highlights the numerous challenges that manufacturing companies face when implementing cloud services.
Lack of control over hardware
When moving to the cloud, manufacturers often lose direct control over the underlying hardware. Traditional on – premise systems allowed for hands – on management of servers and storage, which isn’t the case with cloud hosting. For instance, a mid – sized automotive manufacturing company may be used to customizing its hardware configurations for specific production line applications. Once they shift to the cloud, they rely on the cloud provider’s standard hardware setups, which may not fully align with their unique requirements.
Pro Tip: Before selecting a cloud provider, thoroughly review their hardware specifications and ask about any options for customization or dedicated resources.
Complex migration process
Migrating existing manufacturing data and applications to the cloud can be an extremely complex task. Data from across multiple plants, often in different formats, needs to be aggregated, classified, and then moved to the cloud. A large manufacturing firm with 9+ plants may find it challenging to ensure seamless integration with enterprise systems during the migration. As recommended by AWS, companies should create a detailed migration plan, including a timeline and resource allocation, to minimize disruptions.
Data – backed claim: A recent RightScale report shows that hybrid cloud deployments are up almost 10 percent from last year, and public cloud implementations rose by 25 percent, highlighting the increasing migration activity but also the potential for complexity.
Security and compliance
Manufacturing data, including product designs, production schedules, and customer information, is highly sensitive. Cloud environments need to meet strict security and compliance standards. For example, a pharmaceutical manufacturing company must comply with regulations such as the FDA’s data security requirements. A security breach in the cloud could lead to significant financial losses and damage to the company’s reputation.
Pro Tip: Look for cloud providers that are Google Partner – certified, as they are more likely to adhere to Google’s strict security guidelines.
Difficulty in initial implementation
Setting up cloud services for manufacturing requires a high level of technical expertise. Many manufacturing companies may lack in – house skills to handle the initial configuration. A small – scale electronics manufacturer may struggle to set up a cloud – based production management system due to a shortage of IT staff with cloud implementation knowledge.
Case study: A manufacturing plant implemented a cloud – based digital design and manufacturing system but faced delays in the initial setup, resulting in lost production time and increased costs.
Performance issues
Latency is a crucial metric in cloud hosting as it directly impacts user experience. In manufacturing, it can affect real – time data processing, which is essential for production management. A study of 127 manufacturing facilities found that organizations adopting a certain three – tier approach experienced a 34% improvement in operational efficiency, highlighting the importance of performance in cloud hosting.
Pro Tip: Use a Cloud Performance Benchmark to compare global network performance and connectivity across different cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure.
Vendor lock – in and data integration complexity
Once a manufacturer chooses a cloud provider, it can be difficult to switch to another one due to vendor lock – in. Additionally, integrating data from multiple sources into the cloud environment can be complex. An automotive manufacturer using multiple enterprise software systems may find it challenging to integrate all data into a single cloud platform.
Top – performing solutions include platforms that offer open – source APIs to facilitate data integration and minimize vendor lock – in.
Other cloud – related challenges
There are also other challenges such as connectivity interruptions, which can disrupt production processes. For example, a manufacturing plant in a rural area may face frequent connectivity issues to the cloud, affecting real – time data access. Another challenge is the need for continuous training of employees to use new cloud – based tools effectively.
Try our cloud performance assessment tool to identify potential performance issues in your cloud hosting setup.
Key Takeaways:
- The challenges in cloud implementation in manufacturing are diverse, ranging from hardware control issues to security concerns.
- Proper planning, choosing the right cloud provider, and investing in employee training are crucial for successful cloud adoption.
- Performance and data integration are key factors that can significantly impact the success of cloud hosting in manufacturing.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Did you know that 74 percent of cloud – related transformations in industrial companies fail to capture expected savings or business value (McKinsey)? Overcoming the challenges of cloud implementation is crucial for manufacturing companies aiming to thrive in the digital age.
Integration with existing systems
When transitioning to the cloud, integrating with existing systems can be a major hurdle. A global chemical company planned a multiyear integration program to implement SAP 4/HANA in the cloud, aiming to fold both IT and plant operational technologies. To handle this, they needed to align operations across six continents and meet a tight two – year deadline.
Pro Tip: Start by mapping out your existing systems in detail. Identify the key interfaces and data flows between different applications. This will help you understand the complexity of integration and plan accordingly.
As recommended by leading cloud integration tools, companies can use middleware solutions to facilitate seamless data transfer between on – premise and cloud – based systems.
Scaling and monitoring
Scalability is one of the major advantages of cloud hosting. However, it requires proper monitoring. Latency, a key metric in cloud services, directly impacts user experience, such as the time it takes to load a web page (SEMrush 2023 Study). For example, a manufacturing firm that experiences high traffic during peak production seasons needs to scale its cloud resources to handle the load.
Pro Tip: Implement real – time monitoring tools that can track resource utilization, latency, and other key performance indicators. Set up alerts so that you can scale resources up or down as needed.
Top – performing solutions include cloud – native monitoring platforms like Datadog or New Relic.
Employee training and support
Employees may be resistant to change or lack the skills needed to work with new cloud – based systems. To address this, a manufacturing company could offer comprehensive training programs.
Case Study: A company in the automotive industry introduced a cloud – based system for production management. They provided on – site training, online tutorials, and a dedicated support team. As a result, employees quickly adapted to the new system, and productivity improved.
Pro Tip: Create a training roadmap that includes both initial training and ongoing refresher courses. Encourage employees to get certified in cloud – related technologies.
Addressing compliance
Manufacturing industries are often subject to strict regulations. Ensuring compliance in the cloud is essential. For example, companies may need to adhere to industry – specific data protection laws.
Technical Checklist:
- Identify all relevant regulations that apply to your business.
- Ensure that your cloud service provider is compliant with these regulations.
- Regularly audit your cloud environment for compliance.
Cost – benefit analysis
Before migrating to the cloud, it’s important to conduct a cost – benefit analysis. A McKinsey study shows that building a digital production and logistics cloud platform can deliver over EUR 1 billion in savings and a 30 percent improvement in production efficiency by 2025 for an OEM.
Pro Tip: Consider all costs, including upfront migration costs, ongoing subscription fees, and potential training costs. Compare these with the expected benefits, such as increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
Try our cloud cost calculator to estimate your potential savings.
Multi – cloud and hybrid cloud strategies

According to a recent RightScale report, hybrid cloud deployments are up almost 10 percent from last year, while public cloud implementations rose by 25 percent. Using multiple cloud providers or a combination of public and private clouds can offer flexibility and redundancy.
Comparison Table:
| Cloud Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Multi – cloud | Diversifies risk, access to best – in – class services | Higher management complexity |
| Hybrid cloud | Combines security of private cloud with scalability of public cloud | Integration challenges |
Long – term vision and support
A long – term vision is essential for successful cloud adoption. It’s not just about migrating to the cloud; it’s about continuously evolving and leveraging new cloud capabilities.
Pro Tip: Develop a five – year cloud strategy that aligns with your business goals. Allocate resources for research and development of new cloud – based applications.
Data sovereignty
With data stored in the cloud, concerns about data sovereignty may arise. Different countries have different laws regarding data storage and access.
Case Study: A European manufacturing company needed to ensure that its customer data was stored within the EU due to GDPR regulations. They chose a cloud service provider with data centers in the EU to address this concern.
Pro Tip: Understand the data sovereignty laws of the countries where your business operates. Choose a cloud service provider that can meet these requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- Successful cloud adoption in manufacturing requires careful planning and execution.
- Strategies such as integration with existing systems, proper scaling, and employee training are crucial.
- Addressing compliance, conducting cost – benefit analysis, and having a long – term vision are also essential for a seamless transition.
FAQ
What is cloud hosting for manufacturing?
According to industry standards, cloud hosting for manufacturing involves using remote servers accessed via the internet to store, manage, and process data related to manufacturing operations. It offers scalability, cost – efficiency, and real – time data access. Key components include computing resources like VMs and containers. Detailed in our [Key Components of Cloud Hosting Solution] analysis, it can transform production management.
How to choose the best cloud solution for factories?
First, assess your factory’s specific needs, such as data security, production efficiency goals, and existing IT infrastructure. Compare different cloud providers based on performance benchmarks, reliability, and industry – specific applications. Tools like Google Cloud Platform’s PerfKit Benchmarker can assist. Leading providers include AWS, Azure, and GCP. As recommended by experts, this method ensures a more informed decision.
Steps for integrating cloud services into manufacturing operations
Start by mapping your existing systems to understand data flows and interfaces. Then, choose middleware solutions for seamless data transfer between on – premise and cloud systems. Create a detailed migration plan with a timeline and resource allocation. Regularly monitor and scale resources as needed. This approach, unlike ad – hoc integration, follows a structured process.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) vs Microsoft Azure for manufacturing: Which is better?
Both AWS and Azure offer robust services for manufacturing. AWS has a long – standing reputation and is great for ML pipeline optimization. Azure, on the other hand, integrates well with Windows – based systems. A 2023 SEMrush study shows Azure can lead to more seamless operations in a Windows – centric environment. Consider your existing technology stack when making a choice.